https://philaholisticclinic.com/holistic-approach-to-treatment-of-menorrhagia/
Holistic Approach to Treatment of Menorrhagia
Treatment for menorrhagia
Treatment for menorrhagia is complex but very important. Individualized treatment for menorrhagia is based on specific factors such as:
- Your general health and medical history
- The cause and severity of the disease
- Your tolerance to certain drugs, procedures, or therapies
- The likelihood of your periods getting less heavy soon
- Your future fertility plans
- Effects of the disease on your lifestyle
- Your opinion or personal preference
Medications for heavy periods
The most commonly used medications for menorrhagia are:
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
NSAIDs such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) or naproxen sodium (Aleve) help reduce menstrual blood loss. NSAIDs are also beneficial due to their ability to relieve painful menstrual cramps aka dysmenorrhea.
Tranexamic acid.
Tranexamic acid (Lysteda) helps diminish the amount of menstrual blood loss and should only be consumed at the time of bleeding.
Oral contraceptives.
Additionally to giving birth control, oral contraceptives can help normalize menstrual cycles and lower episodes of extreme or lengthy Menstrual bleeding.
Oral progesterone.
The hormone progesterone can help correct hormonal imbalances and reduce menorrhagia.
Hormonal IUD (Liletta, Mirena).
This IUD releases a type of progestin called levonorgestrel, which thins the lining of the uterus and reduces menstrual flow and cramping.
If you are suffering from excessive menstrual bleeding caused by taking hormonal medications, you and your doctor can treat the condition by changing or stopping your medications.
If your anemia is due to Menstrual bleeding, your doctor may recommend that you take iron supplements on a regular basis. If your iron levels are low but you are not yet anemic, you can start taking iron supplements rather than waiting until you become anemic.
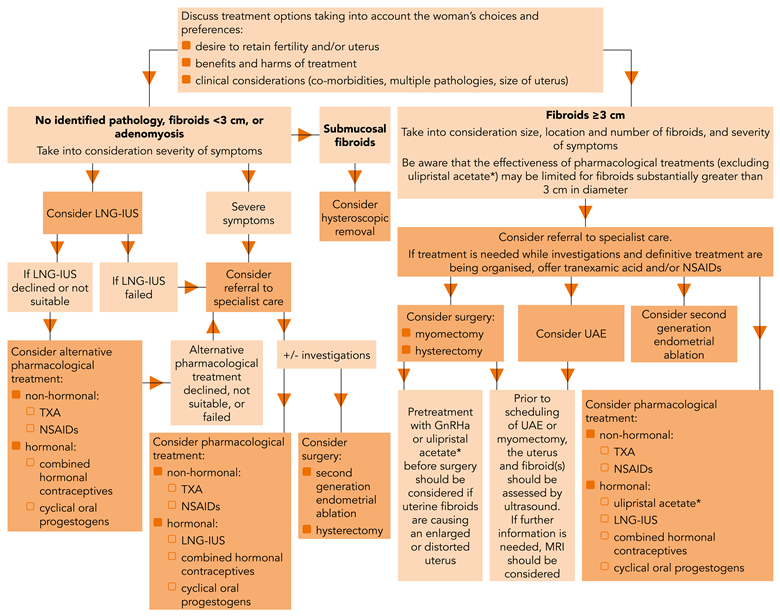
Surgical procedures for the treatment of menorrhagia.
Your condition may require surgical treatment for menorrhagia if pharmaceutical care is unsuccessful. The most common surgical treatment options are:
Dilation and curettage (D&C).
In this procedure, the doctor opens (dilates) the cervix and then scrapes or sucks tissue from the lining of the uterus to reduce menstrual bleeding. Although this procedure is common and often successfully treats acute or active bleeding, you may need additional D&C procedures if menorrhagia recurs.
Uterine artery embolization.
For women whose menorrhagia is caused by fibroids, the goal of this procedure is to shrink fibroids in the uterus by blocking the uterine arteries and cutting off their blood supply. Through the uterine artery embolization, the surgeon inserts a catheter through the femoral artery and leads it to the uterine arteries, where the blood vessels are infused with substances that constrain blood flow to the fibroid.
Focused ultrasound surgery.
Similar to uterine artery embolization, focused ultrasound surgery treats the bleeding caused by fibroids by shrinking the fibroids. This procedure uses ultrasound to destroy fibrous tissue. No incisions are required for this procedure.
Myomectomy.
The myomectomy technique means the surgical elimination of uterine fibroids. Depending on the size, number, and location of the fibroids, the surgeon may choose to undergo myomectomy using open abdominal surgery, through several small incisions (laparoscopic), or through the vagina and cervix (hysteroscopy).
Endometrial ablation.
This procedure destroys (ablates) the lining of the uterus (endometrium). The procedure uses a laser, radio waves, or heat applied to the endometrium to destroy the tissue.
After endometrial ablation, women usually experience considerably lighter Menstrual bleedings. Pregnancy after endometrial ablation is associated with many complications. If you have endometrial ablation, effective or continuous contraception is recommended until the time of your menopause.
Endometrial resection.
For Endometrial resection, an OBGYN practitioner uses an electrosurgical wire loop to cut off the internal lining of the uterus. Both endometrial ablation and endometrial resection benefit women with very heavy menstrual bleeding. Pregnancy after this procedure is not recommended.
Hysterectomy.
Hysterectomy – surgery to remove the uterus and cervix – is an irreversible procedure that causes infertility and stops the menstrual cycle. Hysterectomy is performed under general anesthesia and requires hospitalization. Additional removal of the ovaries (bilateral oophorectomy) can cause premature menopause.
Many of these surgical procedures are performed on an outpatient basis. Although you may need general anesthesia, it is likely that you will be able to return home later in the day. Abdominal myomectomy or hysterectomy usually requires a hospital stay.
When menorrhagia is a sign of another medical condition, for instance, a thyroid disorder, proper management of the initial illness usual outcomes in a reduction of blood loss.
What is menorrhagia?

Menorrhagia definition is pretty simple. Menorrhagia is the medical term for menstrual periods with unusually heavy or prolonged bleeding. Although heavy menstrual bleeding is a common problem, most women do not experience blood loss so severe that it can be described as menstrual bleeding.
Those women that suffer from excessive menstrual bleeding, cannot perform usual daily activities due to excessive blood loss and severe cramps. If you are afraid of your excessive blood loss during the period talk to your doctor. There are many effective treatments for menorrhagia.
What causes heavy periods?
During your menstrual cycle, if an egg is not fertilized, the lining of the uterus breaks down and bleeds. The egg and uterine lining then fall off during your period.

Hormonal problems or conditions that affect the uterus can lead to heavy bleeding and thus become causes of heavy periods.
Other diseases or bleeding disorders can also be the causes of heavy periods.
Very often some forms of imbalance of estrogen and progesterone turn to be causes of heavy periods.
Problems with the uterus that may cause heavy periods are:
- Fibroids (non-cancerous)
- Cancer
- Pregnancy problems (such as miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy)
- Using an intrauterine device (IUD)
Other conditions such as thyroid disorders, kidney or liver diseases, cancer, or blood ailments can also cause heavy periods..
While in some cases the causes of heavy periods are unknown, the most common causes of menorrhagia can be classified as follows:
Hormonal imbalance.
During a typical menstrual cycle, an equilibrium between the hormones estrogen and progesterone controls the development of the lining of the uterus, which is coming off in the course of menstruation. If there is a hormonal imbalance, the lining of the uterus develops excessively and is eventually rejected by heavy menstrual bleeding.
A number of conditions can cause hormonal imbalances, including polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), obesity, insulin resistance, and thyroid problems.
Ovarian dysfunction.
If your ovaries do not release an egg (ovulation) during a menstrual cycle (anovulation), your body does not produce the hormone progesterone as it would during a normal menstrual cycle. This leads to hormonal imbalance and can result in menorrhagia.
Uterine fibroids.
These benign forms of uterus tumors appear during maternity years. Uterine fibroids can cause Menstrual bleeding that is heavier than normal or prolonged.
Polyps.
Small, benign growths in the lining of the uterus (uterine polyps) can cause heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding.
Adenomyosis.
Adenomyosis is the condition that occurs when the endometrial glands invade the muscles of the uterus, often causing heavy bleeding and painful periods.
Intrauterine device (IUD).
Excessively heavy menstrual bleeding is a well-known side effect of the use of non-hormonal intrauterine devices for birth control. Your doctor can help you plan alternative treatment options.
Complications of pregnancy.
Single, profuse, late menstruation may be the result of a miscarriage. Another cause of heavy bleeding during pregnancy includes an unusual placement of the placenta, such as a low placenta or placenta previa.
Cancer.
Uterine cancer and cervical cancer can cause excessive menstrual bleeding, especially if you are postmenopausal or have had an abnormal Pap smear in the past.
Hereditary bleeding disorders.
Some blood disorders such as Von Willebrand syndrome, a disorder in which an essential blood-thickening marker is diminished or compromised can trigger abnormal Menstrual bleeding.
Medicines.
Certain medications, including anti-inflammatory medications, hormone medications such as estrogen and progesterone, and blood thinners, such as warfarin (Coumadin, Jantoven) or enoxaparin (Lovenox), can contribute to heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding.
Symptoms of menorrhagia
Signs and symptoms of menorrhagia are simple and don’t cause any confusion. Often the symptoms of menorrhagia may be similar to other medical conditions or medical problems.

The most common symptoms of menorrhagia are:
- Soak one or more sanitary napkins or tampons every hour for several consecutive hours
- Must use double sanitary guards to control menstrual flow
- Need to get up to change sanitary protection during the night
- Bleeding for more than a week – some women call it a constant period
- Passage of blood clots of more than a quarter
- Limiting daily activities due to heavy bleeding often associated with crams
- Symptoms of anemia, such as fatigue, exhaustion, tiredness, or shortness of breath
Risk factors
Risk factors for heavy periods may be different based on the female’s age and whether or not she has other medical circumstances that could account for menorrhagia. In a normal cycle, the release of an egg from the ovaries stimulates the body’s production of progesterone, the female hormone most responsible for maintaining regular menstrual periods. When no eggs are released, insufficient progesterone can cause heavy menstrual bleeding.
Menorrhagia in teenagers is typically due to anovulation. Teenage girls are especially prone to anovulatory cycles in the first year after their first menstrual period (menarche).
Menorrhagia in older women of reproductive age is typically due to uterine pathology, including fibroids, polyps, and adenomyosis. Nevertheless, other medical conditions such as uterine cancer, blood disorders, side effects from medication used, and liver or kidney illnesses may become contributing factors.
The differential diagnosis for menorrhagia
Your OBGYN physician will most likely ask about your medical history and your menstrual cycles. You may be asked to keep a diary of the days with bleeding and the days without bleeding, including records of how severe the discharge was and what hygiene measures were needed to keep it under control.
Your gynecologist will perform a physical examination and may recommend one or more tests or procedures, such as:
Blood tests.
The blood sample can be tested for iron deficiency (anemia) and other conditions, such as thyroid disease or blood clotting disorders.
Pap smear.
This test collects cells from the cervix and tests for infection, inflammation, or changes that could be cancerous or lead to cancer.
Endometrial biopsy.
Your doctor may take a tissue sample from inside the uterus for a pathologist to examine.
Ultrasonic.
This test creates images of your uterus, ovaries, and pelvis based on reflection of the currents of ultrasound from your abdominal organs.
Based on the outcomes of initial tests, your gynecologist may propose further testing techniques, such as:
Sonohysterography.
During Sonohysterography, a fluid solution is instilled into the uterus through a tube that is inserted into the female’s vagina and cervix. The medical provider will then use ultrasound to look for problems in the lining of the uterus.
Hysteroscopy.
Hysteroscopy assumes an insertion of a thin and light device into the uterus through the vagina and cervix that allow OBGYN practitioner to observe the condition of the uterus.
Natural treatment for menorrhagia

Once the serious issues are ruled out, you can focus on the natural balance of your hormones.
Let’s discuss.
Improving gut health may be a viable strategy of treatment for menorrhagia.
Gut imbalances, such as bacterial dysbiosis or inflammation caused by consuming processed foods, are seen as stress on your body. This low underlying stress level can deplete your sex hormones to produce stress hormones instead. High levels of stress have also been shown to increase leaky gut.
Other research indicates that your hormones are also affected by these gut-related problems:
- Poor digestion of fats
- The diversity and balance of intestinal bacteria
- The microbiome of the female reproductive tract
- This means that supporting gut health can likely help rebalance any hormonal menorrhagia causes.
All of this evidence suggests that a healthy gut microbiome improves hormone levels and reduces susceptibility to hormone-related disorders, including some causes of menorrhagia.
Heavy period diet – an essential part of any treatment for menorrhagia
Blood sugar imbalances are associated with increased hormonal symptoms such as PMS and painful periods. This is likely due to the fact that frequent fluctuations in blood sugar levels are perceived by the body as stress. What you eat also affects the level of gut inflammation, which is also considered stressful for your body.
A simple whole food diet without inflammatory or processed foods, such as the paleo diet, can help reduce heavy menstrual bleeding. This is because the Paleo diet follows four principles of healthy eating. Eating a real food anti-inflammatory diet reduces the causes of many hormonal imbalances by improving your gut health, reducing inflammation, and keeping your blood sugar stable.
Supplements for the treatment for menorrhagia
If you are suffering from menorrhagia, it is critical to make some diet adjustments to improve your condition.
Consider the following suggestions:
Eat a diet that is high in the following: vegetables, fruits high in vitamin C, whole grains, legumes, fish high in omega-3 oils, nuts, seeds, and foods rich in iron such as brewer’s yeast, and wheat germ Molasses.
Cut down on saturated animal fats (beef, chicken, dairy products) to support good prostaglandin formation.
Eat more organic products, especially organic meat. Otherwise, you’re adding hormones, antibiotics, and other chemicals to your body that are likely to make menorrhagia worse.
Eliminate food intolerances as they are known to cause inflammation in the body that can make menorrhagia worse.
Avoid alcohol as consuming it can increase inflammation and worsen your symptoms.
Flavonoids and vitamin C.
In healthy women, capillary integrity decreases both after ovulation and before menstruation. Flavonoids and vitamin C improve capillary integrity and have been shown in studies to reduce menorrhagia. In addition, bioflavonoids can occupy estrogen receptor sites on the uterus, thereby reducing the estrogen-stimulating effect on the endometrium. This, in turn, can reduce menstrual blood loss. Consequently, women with menorrhagia may need more vitamin C and bioflavonoids than the average woman. Vitamin C also helps in the absorption of iron. Note that vitamin C supplementation alone is not as effective as using it in combination with bioflavonoids.
Iron:
While it is well known that heavy Menstrual bleeding can lead to iron deficiency anemia, it is not so well understood that iron deficiency anemia can actually cause or aggravate Menstrual bleeding. Iron deficiency can cause the muscles of the uterus to weaken, thereby reducing the ability of these muscles to constrict blood vessels, which is necessary to reduce or stop bleeding. Heavy bleeding can then worsen iron deficiency, which in turn makes bleeding worse, thus creating a vicious cycle. Therefore, it is very important to gain access to iron deficiency anemia when treating patients with menorrhagic bleeding and to have adequate iron supplementation.
Vitamin A:
Research has shown that a lack of vitamin A affects hormone production and enzyme activity in the ovaries of animals. While the process of action of vitamin A on Menstrual bleeding is uncertain, experiments have shown that it has a complex interaction with estrogen. For example, the administration of estrogen has decreased serum vitamin A levels in these animals. In addition, women with menorrhagia have been found to have lower serum vitamin A levels than healthy women. Note that a lack of vitamin C, zinc, protein, or thyroid hormone can interfere with the conversion of carotenes to vitamin A, creating a deficiency in vitamin A.
B Vitamins:
The research paper has shown that a shortage of B vitamins affects the liver to fail its ability to deactivate estrogen, which could supposedly result in an overflow of estrogen. As some forms of menorrhagia are caused by excess estrogen, supplementing with B vitamins can restore the liver’s ability to properly metabolize estrogen, thus reducing menstrual flow.
Vitamin E:
This vitamin diminishes the capillary vulnerability and promotes the production of helpful prostaglandins.
Vitamin K:
Although vitamin K deficiency is quite rare, its role in the manufacture of clotting factors has clear implications for the treatment of menorrhagia. However, consumption of supplemental vitamin K has also been demonstrated to reduce excessive blood loss in females without a known coagulation condition, so it may be prudent to include Vitamin K in a treatment plan.
Ginger:
Menorrhagia is believed to be due to an altered prostaglandin-2 ratio and ginger has been shown to inhibit enzymes related to this altered ratio: prostaglandin synthetase and cyclooxygenase.
Vitex Agnus Castus (Chaste Tree):
This is perhaps the most famous herb in all of Europe for managing hormonal imbalances in women. It acts on the hypothalamus and pituitary gland to increase LH production and slightly inhibit FSH release. This causes a change in the estrogen/progesterone ratio, thus helping to reduce menstrual flow. Vitex has also been shown to inhibit the release of prolactin from the pituitary gland, especially when a woman is under stress. This herb may take 4 to 6 months to take effect.
Home remedies for heavy periods – the most common treatment for menorrhagia
In addition to working with a doctor, certain home remedies for heavy periods can help reduce symptoms and relieve heavy menstruation. Scientific studies have shown that people can help regulate irregular menstrual periods through home remedies and lifestyle changes such as changing diet and exercise regimes.

Some women can also try other home remedies for heavy periods, such as eating food spiced with turmeric or pineapple, even though there is no scientific proof that these methods work.
This section describes which home remedies for heavy periods can help with irregular excessive menstruation, which treatment options have no evidence to support them, and how to use them.
Reduce stress
Scientists indicate that elevated levels of emotional stress are related to irregular and heavy periods.
Discovering methods to decrease stress levels can help women control their menstrual cycle regularity and quality. Avoiding stressful situations and managing family or workplace expectations can help.
When stress cannot be avoided, try to engage in activities that limit the impact it has on the body.
Meditation
Meditation is a free and easy way to reduce stress at home or at work. Since stress and heavy periods are related, lowering the level of stress can make periods lighter.
Researchers suggest that meditation can ameliorate multiple negative effects of psychological stress.
To perform meditation:
- find a quiet place to sit
- sit straight, with your arms relaxed and your hands on your knees
- inhale and exhale deeply
- focus on the sound of the breath
- listen to other surrounding sounds
- acknowledge the thoughts as they arise, but then let them go
At first, try to meditate for just a few minutes and increase the time by one minute each day.
Yoga – a great addition to any form of treatment for menorrhagia
Yoga is an exercise-based type of meditation that most women can perform in the comfort of their homes. Many people around the world use this ancient practice on a daily basis to improve their well-being.
Practicing yoga can be an effective way to regulate your periods. A small-scale 2013 study found that daily yoga practice helped balance hormones associated with heavy periods.
Bring your weight to normal as a part of treatment for menorrhagia
Changes in body weight can affect a person’s menstrual cycle.
Having a low body weight can mean that a person’s periods become irregular or even stop. The body needs some fat to make menstrual hormones, so gaining weight can help regulate your cycle.
Similarly, being obese or just overweight can cause menorrhagia. Losing weight can make a person’s periods more regular.
Retaining a healthy weight is vital for women’s health. Eating a healthful, low-calorie diet and exercising regularly can help a person manage their weight.
Exercises in addition to all other approaches to the treatment of menorrhagia
Exercise is vital to a person’s mental and physical health. Research suggests that regular aerobic exercise can improve menstrual cramps.
Exercises are an efficient method to retain a healthy weight. As being overweight can cause irregular periods, weight reduction can make periods more regular.
However, when it comes to exercises and periods, balance is important. Exercising too much can interrupt your menstrual cycle. Extreme exercise can even cause a person’s periods to stop.
The Department of Health and Human Services recommends that adults get at least 2.5 to 5 hours of moderate-intensity exercise or half that amount of vigorous-intensity activity every week.
Acupuncture for heavy periods – an ancient Chinese natural treatment for menorrhagia
Acupuncture is very effective in helping to reduce the flow of a heavy period. Traditional Chinese Medicine has been helping to manage women’s periods for over 2,500 years. Menstrual bleeding or heavy bleeding is often seen in the early perimenopause and adolescence period when hormone levels fluctuate and progesterone levels decline and estrogen levels rise. Acupuncture heals excess estrogen that causes heavy menstrual bleeding. Anemia is often observed with profuse bleeding, as a result of which women complain of severe fatigue. Acupuncture is the best remedy for excessive bleeding.

Best acupuncturist near me
In order to select the best acupuncturist near me, it is important that the acupuncturist has at least seven-ten years of experience.
You can also google for the best acupuncturist near me, or ask your PCP to refer to an experienced acupuncturist. Once you find the acupuncture clinic in your area, you can first look at their reviews on Google and then make an appointment with the doctor if you are satisfied with the reviews.
The acupuncturist will talk about your concerns and help you feel more comfortable before your first session. Acupuncture usually takes multiple sessions to get a noticeable result for any disease, but within 3 or 4 sessions, patients may feel positive changes.
Homeopathic remedies for heavy periods – the #1 natural treatment for menorrhagia
Homeopathy for heavy periods is effective and safe. Different homeopathic remedies for heavy periods are successfully used during menstruation. Homeopathic remedies for heavy periods can entirely cure women who are experiencing heavy periods. To ensure that a woman suffering from heavy menstrual bleeding receives proper homeopathic treatment, there are several key features to consider. The first thing to notice is the color of the blood: light red, pale, dark, or black. It’s also important to know about the fluidity of the blood – whether the blood is fluid, clotted, or both. Another feature to look out for is whether the blood flow is oozing, squirting, or different or whether there is bleeding associated with pain. These are important points to keep in mind before recommending homeopathic remedies for heavy periods. The homeopath will also ask about additional symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, loose stools, and headache to properly choose homeopathic remedies for heavy periods.

The most common homeopathic remedies for heavy periods are:
Premenstrual problems with limb swelling, fluid retention, and bloating often indicate the need for this remedy. The woman may feel very awkward and clumsy, and keep dropping things because her hands feel swollen. Diarrhea that occurs around the time of menstruation strongly suggests this remedy.
PMS with tiredness, anxiety, and a feeling of being overwhelmed suggest the need for this remedy. The woman may have problems with water retention and weight gain, tender breasts, indigestion, and headaches. The period is often too early and too long, sometimes with a flow of bright red blood. General shivering with clammy hands and feet as well as cravings for sweets and eggs are further signs of Calcarea.
Women in need of this remedy are usually intense and have a tremendous need for an outlet, both physical and mental. Symptoms of PMS include congestion, headache, hot flashes, hot flashes, and pronounced irritability – often with strong feelings of distrust or jealousy. When the flow arrives, it can be difficult, but it creates tension. An intolerance to restrictive clothing around the waist or neck is another sign of Lachesis.
PMS with sweet cravings and cravings (sometimes a bulimic tendency) suggests the need for this remedy. Indigestion with gas and gas is often seen, with the person feeling worst in the late afternoon and evening. Menstruation may be delayed, followed by heavy blood flow that persists for additional days. In need of this remedy, women often look concerned and lack confidence – although they can be irritable and bossy around pets and family members. The desire to be alone but with someone in the other room is another indication of Lycopodium.
The person who needs this measure usually seems reserved for others but is deeply emotional on the inside. Those women may experience extreme sadness and feel lonely, but they don’t feel hurt or angry when others try to comfort them or sympathize with them. Depression, anger over little things, and the need to be alone to cry are often seen when the Natrum wall is needed. Menstrual problems can be accompanied by migraines or back pain, which improves when you lie on something hard or press a hard object into a sore spot. Salt hunger, strong thirst, and a tendency to worsen after being in the sun are other indications for using this remedy.
This drug can be helpful for many conditions related to hormonal changes and is often helpful for girls who have recently started their periods. PMS is typical with irritability, mood, and tearfulness. Your menstrual bleeding may be delayed or stopped if you feel sick, nauseous, and faint. Too warmth or breathlessness makes the situation worse, and fresh air can provide relief. The time, amount, and nature of menstruation vary as do a woman’s moods when Pulsatilla is the cure. A woman is usually emotional and needy, she needs a lot of attention and comfort.
Indications for this remedy include great premenstrual irritability (which causes other people to “walk on eggs”) and crampy pain with a sinking sensation during periods. The woman may feel as if her uterus is pushing out and she may need to sit a lot or cross her legs. This kind of woman is likely to feel worse from intense emotions or excitements and better outdoors.
This remedy may be indicated when a woman has an irregular period with constricting pain that may extend to the rectum or the area above the tailbone. Women tend to be impatient, irritable, and easily offended. Colds and constipation are also common. Mental strain, anger, physical exertion, stimulants, strong foods, and alcohol can make things worse. Warmth and rest often help.
This remedy relieves abundant and painful periods with red blood clots and pain that spreads to the root of the thighs.
Indications for this remedy include painful, late, or repressed menstruation, sometimes with the feeling that the pelvic floor is weak or as if the uterus is sagging. The female may feel petulant, and sad, for the time being losing interest in spousal and family relations, wishing to be left alone. Humidity, sweating, and housework can aggravate symptoms. Heat and exercise, especially dance, often brighten a woman’s gaze and restore some energy.
Menstrual bleeding with heavy flow and cramps, along with a sensation of tiredness and fatigue, chill, and even vomiting and diarrhea, are indications for this remedy. Periods can start too early and last too long. Discomfort is often worse at night and even in wet, cold weather. Hot drinks, exercise, or bowel movements can make things worse. Small meals, cold drinks, and wrapping up in warm clothes or blankets will tend to bring relief.
In addition to our own clinical experience in treatment for menorrhagia, extensive studies in Germany and the UK have confirmed the use of homeopathic remedies for heavy menstruation. Safe, simple, and natural homeopathy is especially beneficial for women as it is the only medical system that understands the emotional and psychological support that is critical to recovery. Gentle yet effective, it offers a painless and long-lasting solution to any menstrual problem.
Natural treatment for menorrhagia in Philadelphia
If you are one of those women that suffer from chronic heavy periods and need natural help to handle the excessive bleeding and avoid complications such as fatigue, pain, anemia, etc., contact Philadelphia Holistic Clinic (267) 284-3085 and schedule an appointment for a holistic evaluation with Dr. Tsan. At the clinic, we have different specialists that would help you to get rid of this problem and possibly cure you once and forever. Our clinic is kind of universal and we provide all forms of holistic treatments in one place.
Comments
Post a Comment