Treatment for interstitial cystitis
Treatment for interstitial cystitis is always a challenge. No simple therapy eliminates the signs and symptoms of interstitial cystitis, and also no one treatment works for everybody. You may require to attempt various treatments or mixes of therapies prior to you discover a technique that eases your symptoms.
Physical therapy

Dealing with a physical therapist might relieve pelvic discomfort related to muscular tissue tenderness, restrictive connective tissue, or muscle mass irregularities in your pelvic flooring.
Oral medications
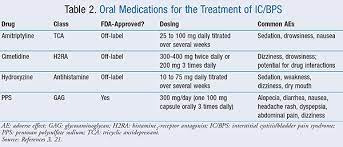
Oral drugs that may enhance the signs and symptoms of interstitial cystitis include:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications, such as Ibuprophen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) or naproxen salt (Aleve), to alleviate pain.
- Tricyclic antidepressants, such as amitriptyline or imipramine (Tofranil), assist relax your bladder and also block pain.
- Antihistamines, such as loratadine (Claritin, others), may reduce urinary system seriousness and also regularity as well as soothe other signs.
- Pentosan polysulfate salt (Elmiron), which is accepted by the Food and Drug Administration especially for dealing with interstitial cystitis. Exactly how it functions is unidentified, however, it may restore the inner surface area of the bladder, which safeguards the bladder wall surface from substances in urine that could irritate it. It might take 2 to four months prior to you begin to feel pain relief and up to six months to experience a decrease in urinary system frequency.
Nerve stimulation.
Electrical nerve stimulants, also known as neuromodulators, send weak electrical impulses to the nerves in the lower back and help control urinary function or relieve chronic pain. Neuromodulators have proven to be beneficial for many patients with interstitial cystitis who do not receive sufficient relief from other treatments.
Some neuromodulators are worn externally. Others are surgically implanted devices. Most implanted neuromodulators work by sending weak electrical impulses to the nerves in the lower back. These nerves, called sacral nerves, affect the bladder and surrounding muscles that control urinary function. Before surgery, under the skin, usually, in the lower back, a test stimulation is performed. Only patients who respond positively to the test stimulator are considered for permanent implants. Learn more about neuromodulation for people with IC.
Transcutaneous electric nerve stimulation (TENS).
With TENS, moderate electrical pulses relieve pelvic pain as well as, sometimes, reduce urinary frequency. 10S may increase blood flow to the bladder. This may strengthen the muscular tissues that assist control the bladder or cause the launch important that obstruct pain.
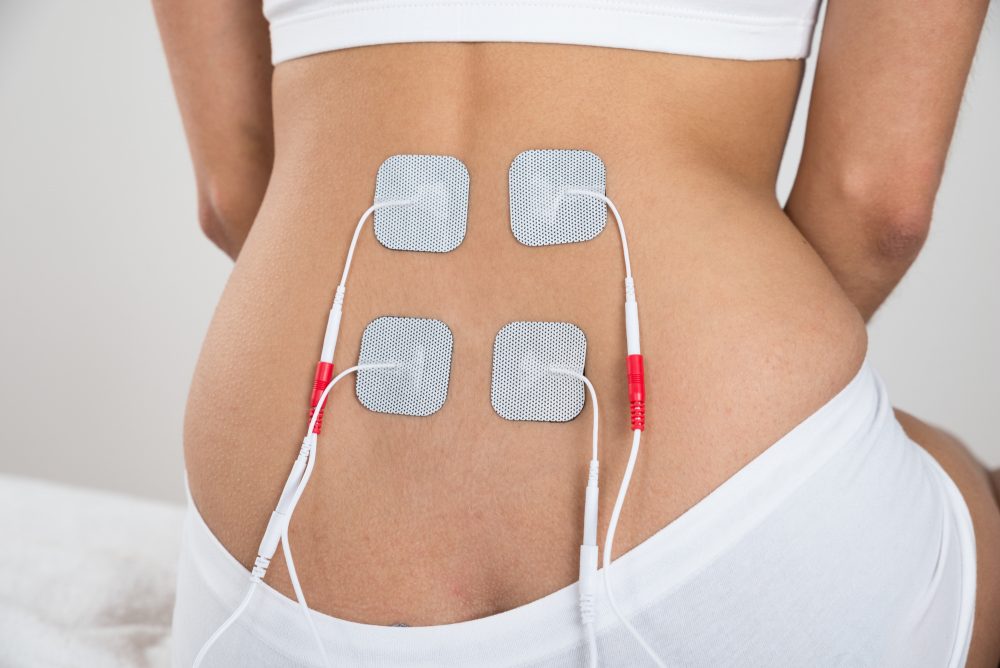
Electrical cables positioned on your lower back or simply above your pubic area deliver electrical pulses– the length of time, as well as the frequency of therapy, relies on what jobs best for you.
Sacral nerve stimulation.
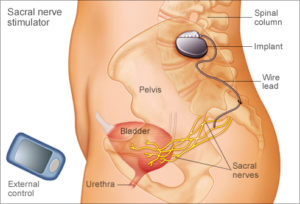
Your sacral nerves are a key link between the spine and also nerves in your bladder. Stimulating these nerves may minimize urinary system seriousness associated with interstitial cystitis.
With sacral nerve excitement, a slim cord positioned near the sacral nerves sends out electric impulses to your bladder, similar to what a pacemaker does for your heart. If the treatment lowers your symptoms, you may have a long-term tool surgically implanted. This treatment does not take care of pain from interstitial cystitis, yet might assist to soothe some signs of urinary frequency and necessity.
Bladder distention

Some people see a short-lived improvement in signs after cystoscopy with bladder distention. Bladder distention is the stretching of the bladder with water. If you have lasting improvement, the procedure may be duplicated.
Medicines instilled into the bladder
In bladder instillation, your doctor positions the prescription medication dimethyl sulfoxide (Rimso-50) into your bladder through a slim, versatile tube (catheter) placed with the urethra.
The option in some cases is mixed with various other medications, such as an anesthetic, and also continues to be in your bladder for around 15 mins. You urinate to expel the option.
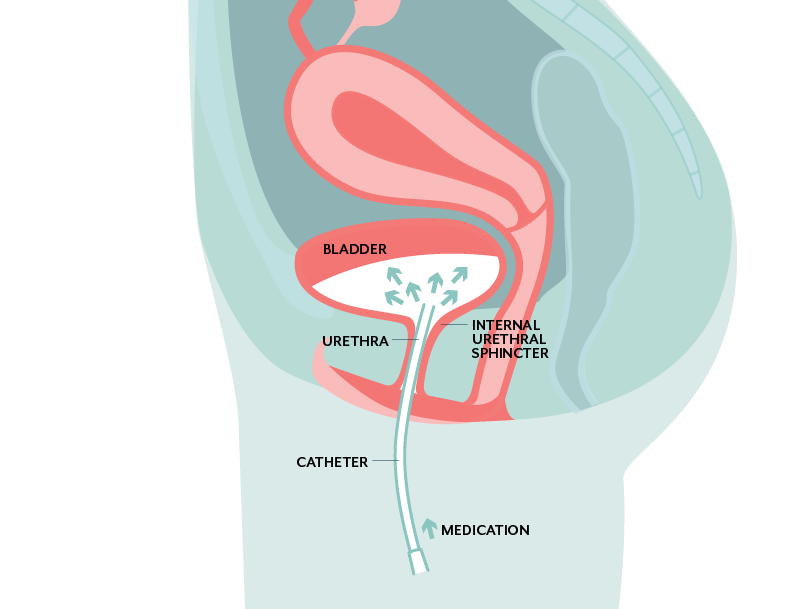
You might receive dimethyl sulfoxide– likewise called DMSO– therapy regularly for six to 8 weeks, and then have maintenance treatments as required– such as every couple of weeks, for up to one year.
A more recent approach to bladder instillation utilizes a service including the medicines lidocaine, sodium bicarbonate, and also either pentosan or heparin.
Surgical treatment for interstitial cystitis
Physicians hardly ever use surgical treatment to deal with interstitial cystitis due to the fact that getting rid of the bladder doesn’t ease pain and also can lead to various other difficulties.
People with serious discomfort or those whose bladders can hold just extremely small volumes of pee are possible prospects for surgery, however usually just after other therapies fall short, and also signs influence lifestyle.
Surgical alternatives consist of:
Fulguration.
This minimally intrusive method involves the insertion of tools with the urethra to burn off ulcers that may be present with interstitial cystitis.
Resection.
This is an additional minimally intrusive method that includes the insertion of tools through the urethra to reduce any type of abscess.
Bladder augmentation.
In this treatment, a surgeon raises the ability of your bladder by putting a spot of an intestinal tract on the bladder. However, this is carried out only in very specific as well as unusual circumstances. The treatment does not get rid of discomfort and some individuals require to clear their bladders with a catheter many times a day.
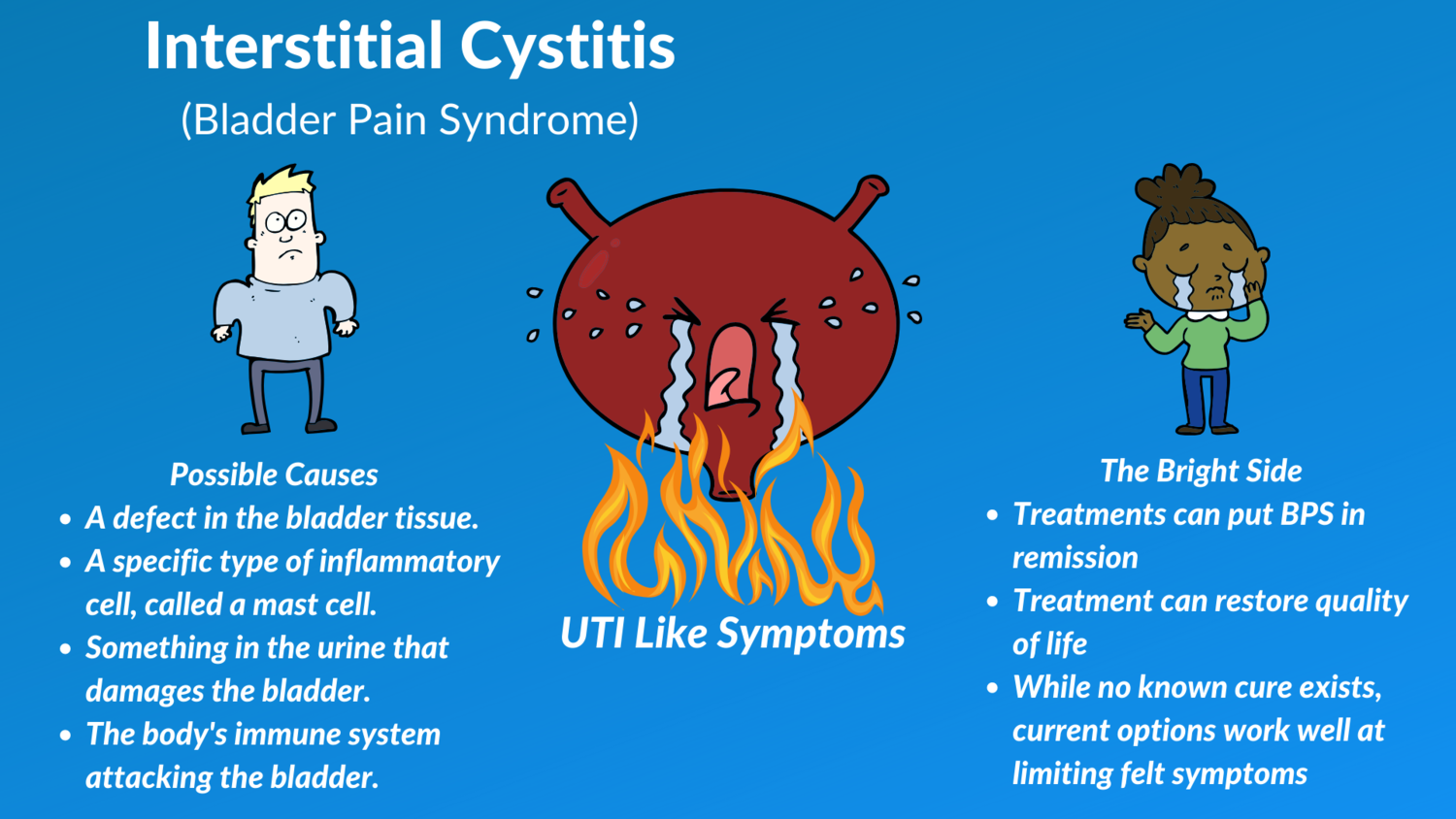
What Is Interstitial Cystitis (IC)?
It is a chronic condition that is accompanied by bladder pain and pressure and, at times, even pelvic pain. The pain intensity can be mild to severe. For some people, IC symptoms can flare up and subside after some time, while others can experience constant pain. IC symptoms are quite similar to Urinary Tract Infection symptoms; however, the difference is that IC shows no sign of infection, bacteria, and antibiotics prove to be inept in managing the pain. IC can affect both genders but is more prevalent among women.
Currently, IC doesn’t have a cure, so treatment primarily aims to minimize the symptoms of pain, urgency, and frequency. Successful reduction of these symptoms can allow IC patients to live comfortable lives.
You’ll have to try out various remedies before finding the right treatment for your symptoms. There are various natural remedies, and Home treatment for interstitial cystitis can also prove to be beneficial.
Diagnosis of interstitial cystitis.
Bladder diary and medical history.
Your physician will ask you to describe in detail the symptoms you are experiencing and may ask you to keep a bladder journal, recording the volume of fluids you drink and the amount of urine that passes.
Pelvic examination.
During a pelvic exam, the doctor examines the external genitals, the vagina, and the cervix and palpates the abdomen to assess the internal pelvic organs. Your doctor can also examine your anus and rectum.
Urine test.
A specimen of your urine will be evaluated for signs of urinary tract infection (UTI).
Cystoscopy.
The urologist inserts a thin tube with a tiny camera (cystoscope) through the urethra, showing the lining of the bladder. The doctor may also inject fluid into the bladder to measure the bladder capacity. Also, the urologist may execute this procedure, known as hydrodistension after you have been numbed with an anesthetic drug to make you feel more comfortable.

Biopsy.
During anesthesia cystoscopy, the urologist specialist may extract a small tissue sample from the wall of the bladder and urethra for a microscopic inspection. This test is to rule out bladder cancer and other rare roots of bladder pain.
Urine cytology.
Your doctor collects a urine sample and tests the cells to rule out cancer.
Potassium sensitivity test.
The doctor places (drops) two solutions – water and potassium chloride – in the bladder, one at a time. You are asked to rate the pain and urgency you feel after each solution has been vaccinated on a scale of 0 to 5. If you feel noticeably more pain or a sudden need after using a potassium solution, your doctor may diagnose interstitial cystitis. People with normal blisters cannot tell the difference between the two.
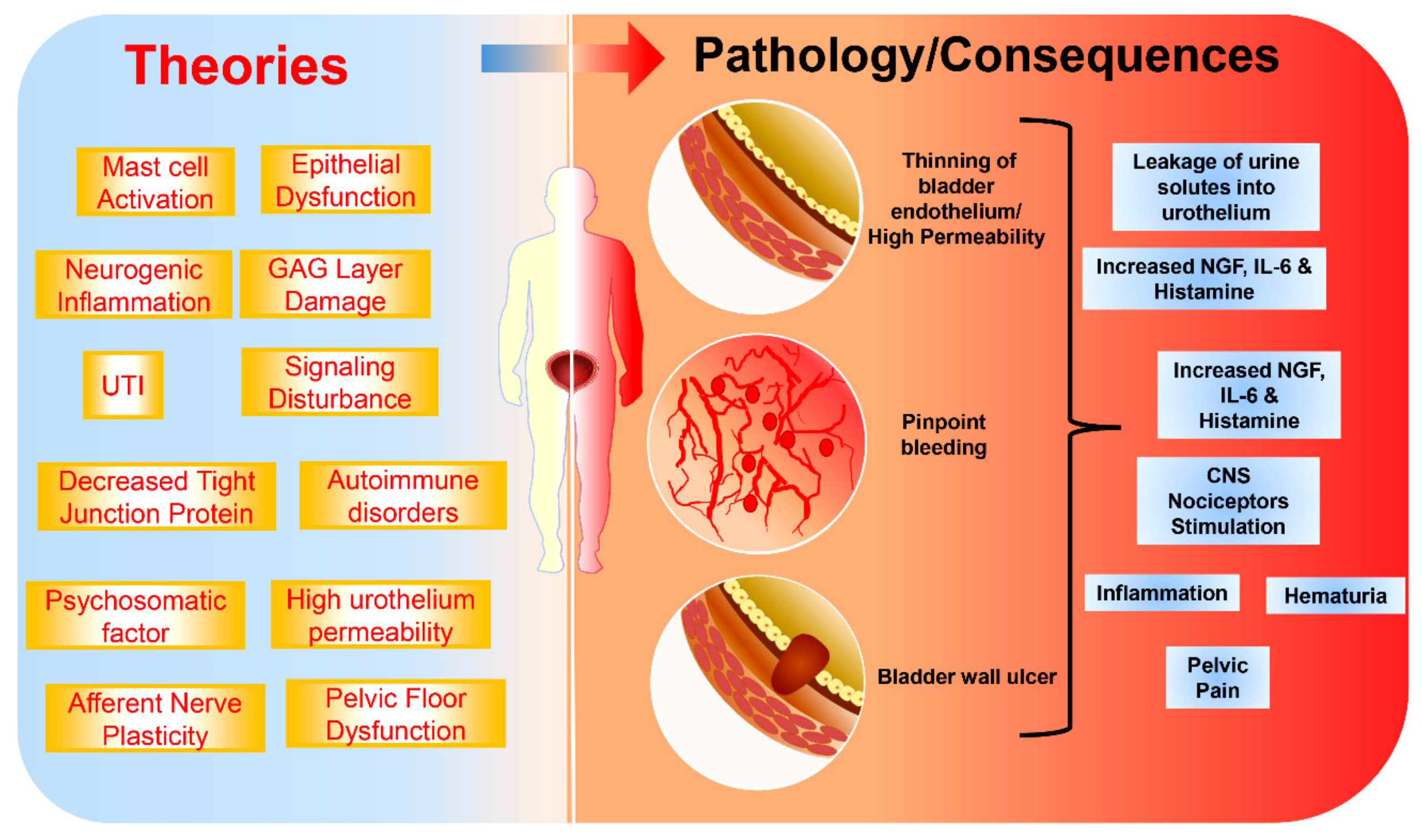
Causes of interstitial cystitis.
The exact causes of interstitial cystitis are unknown, but it is likely that many factors contribute to it. For example, people with interstitial cystitis may also have a defect in the protective membrane (epithelium) of the bladder. A leakage in the epithelium of the internal lining of the bladder can allow toxic constituents in the urine to irritate the cells of the bladder wall.
Other possible but unproven factors include autoimmune reactions, heredity, infection, or allergies.
Risk factors of interstitial cystitis.

These factors are associated with an increased risk of interstitial cystitis:
Your sex.
Women are diagnosed with interstitial cystitis more often than men. Symptoms in men can mimic interstitial cystitis but are most often associated with inflammation of the prostate (prostatitis).
Your skin and hair color. Having fair skin and red hair has been associated with an increased risk of interstitial cystitis.
Your age.
Most people with interstitial cystitis are diagnosed in their 30s or older.
Having a chronic pain disorder.
Interstitial cystitis may be associated with another chronic pain disorder, such as irritable bowel syndrome or fibromyalgia.
Symptoms of Interstitial cystitis.
Symptoms of interstitial cystitis diverge from person to person.
If you are suffering from interstitial cystitis, symptoms may change over time, periodically erupting in response to common triggers such as menstruation, prolonged sitting, stress, exercise, and sexual activity.

Signs and symptoms of interstitial cystitis include:
- Pain in the pelvis or between the vagina and the rectum in women
- Pain between the scrotum and anus in men (perineum)
- Chronic pelvic pain
- A persistent, urgent need to urinate
- Frequent urination, often in small amounts, during the day and night (up to 60 times a day)
- Pain or discomfort when your bladder fills up and relief from urinating.
- Pain during sexual intercourse.
The severity of symptoms varies from person to person, and some people may experience asymptomatic periods.
Although the signs and symptoms of interstitial cystitis may resemble those of a chronic urinary tract infection, there is usually no infection. Nevertheless, symptoms of interstitial cystitis may deteriorate if a patient with interstitial cystitis gets a urinary tract infection.
Home treatment for interstitial cystitis
Home treatment for interstitial cystitis is safe and effective. For the treatment of interstitial cystitis, conventional medications are generally prescribed. However, at times they can lead to adverse effects and make symptoms worse. There’s no cure for the condition as of now, making treatment even more complicated and difficult to find. The right treatment can suppress the symptoms to such an extent that it doesn’t bother your life in any way.

Some studies show that natural and alternative treatments can provide great relief. Natural remedies for interstitial cystitis are generally safe and can provide life-long relief.
Natural remedies for interstitial cystitis – the most common natural treatment for interstitial cystitis.
The good news is that there are various natural and home remedies for interstitial cystitis that can manage your symptoms. Many of these are backed by science as well. They might take some time to show results but are significantly safer and more affordable.
Healthy Diet – an essential part of any treatment for interstitial cystitis

Changing your diet is an effective home treatment for interstitial cystitis and can prove to be very beneficial. There is no particular diet for IC patients, so you might want to work with a nutritionist to find the right plan. Generally, it’s recommended that you eliminate caffeine, alcohol, sugar, soy, and other processed fats, carbohydrates, and food additives. Instead, incorporate more foods that are low in histamine, oxalate, and FODMAPS. Acidic fruits like cranberry should also be avoided.
Stress Management – an important part of treatment for interstitial cystitis

If you’re looking for potent Home treatment for interstitial cystitis, stress management should be a key priority. Studies show that reducing stress can, in turn, lead to a reduction in bladder inflammation. Stress can induce free radicals and inflammation in your body, so reducing free radicals and oxidation can aid in managing IC symptoms. Additionally, some studies show that there might be a link between IC flare-ups and cortisol levels.
If you want to reduce your stress levels, you can partake in 30-40 minutes of daily low-impact exercise, getting a massage, seeing a therapist, or joining a support group.
Heat/Cold Therapy – physical treatment for interstitial cystitis
For relieving pain from interstitial cystitis flare-ups, heat/cold therapy can be an effective Home treatment for interstitial cystitis. Depending on the type of your flare-up, you can opt for cold or heat or maybe even a combination of both. Muscle and bladder wall flares can be effectively treated with heat. The simplest way would be to place a hot water bottle or heating pad over your abdomen whenever your bladder experiences spasms. Heat therapy will soothe your bladder and aid in relaxing tense and spamming muscles.
For a pelvic floor flare, numbing the area can be useful. For severe urethra burning, placing a cold water bottle against your urethra can be a potent Home treatment for interstitial cystitis.
Supplements – another effective treatment for interstitial cystitis
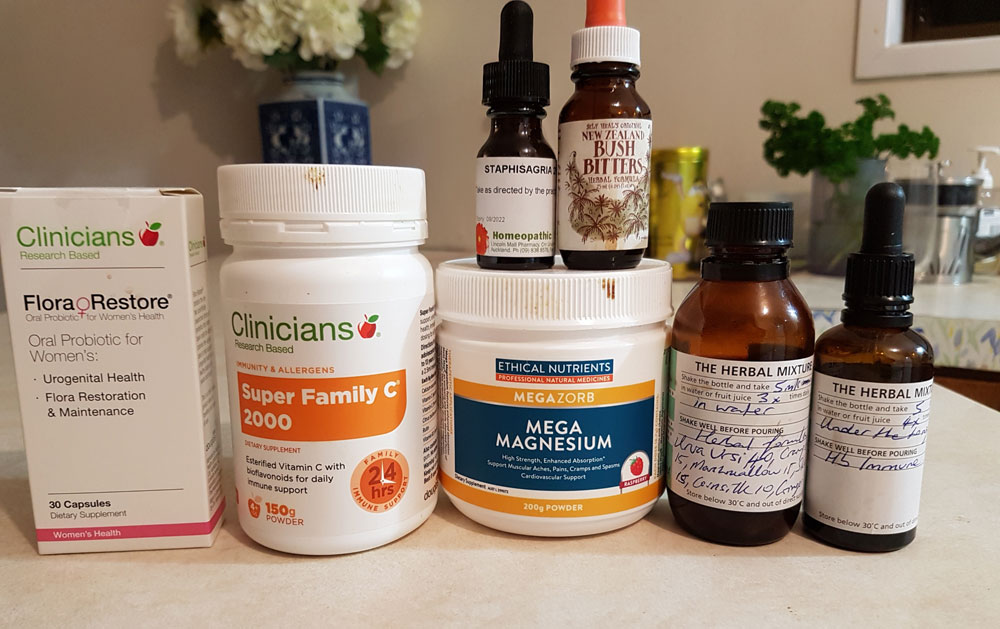
Certain supplements can be useful in managing your interstitial cystitis symptoms. Calcium glycerol can reduce the acidity of your food, and L-arginine can relax your bladder. Aloe vera is also helpful in rebuilding your bladder’s mucous layer, which is left damaged by IC for many patients. Melatonin can also protect your bladder from irritants.
Homeopathy – best natural treatment for interstitial cystitis
Homeopathy has time and again proved that its very effective in managing chronic conditions. Homeopaths carry out an intensive evaluation of past and present conditions to get to the root of the problem before prescribing remedies. It can provide life-long results. Homeopathy incorporates various natural remedies for interstitial cystitis such as Kali Carb, Sarsaparilla, Lycopodium, Cantharis to help manage various interstitial cystitis symptoms.
Another huge advantage is that the remedies are natural; there are minimal or no side effects. For some patients, homeopathy can provide better results where even conventional methods fail.
Acupuncture – great ancient Chinese natural treatment for interstitial cystitis
Many interstitial cystitis patients have witnessed tremendous improvement after trying out acupuncture. After intensive evaluation, acupuncturists place very thin needles in strategic points of your body. It has been documented to be very useful in dealing with bladder pain syndrome, IC, and even bladder infections. As stress can lead to inflammation, acupuncture can be of tremendous help in lessening stress levels. The chances of side effects are also minimal, and acupuncture can be beneficial in improving the overall quality of life.
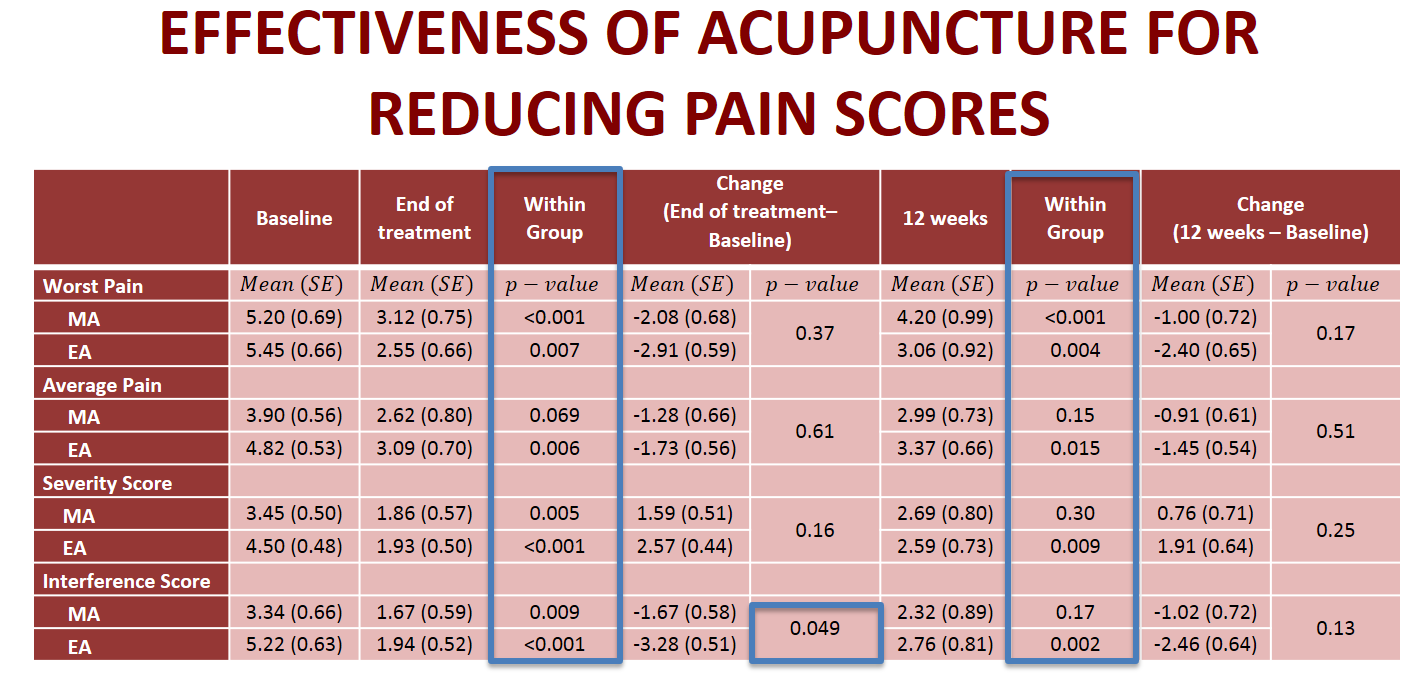
AE showed greater improvement in pain interference, muscle sensitivity of the pelvic floor, with continuous effects on pain scores at 12 weeks compared to MA. This study demonstrates that patients tolerate and improve with weekly sessions of acupuncture treatment and that AS, specifically, can improve the quality of life of women with PBS.
Physical Therapy for interstitial cystitis
Pelvic floor dysfunction is also common with many IC patients. In this case, physical therapy as a Home treatment for interstitial cystitis can help alleviate the pain. IC patients are plagued by constant pain and discomfort, which will tighten up the muscles of your pelvis. This can make urination uncomfortable. Physical therapy can aid in the relaxation of your pelvis and core strengthening. You should consult a physical therapist to find the right solution for your symptoms.
Natural remedies for interstitial cystitis are generally safe and are a far more affordable option. They can help manage your symptoms considerably and provide significant relief. In combination with other remedies or treatments, the effects can be even more profound.
Conclusion
IC symptoms can be very frustrating and challenging to manage. However, the right natural treatment for interstitial cystitis and customized natural remedies for interstitial cystitis can alleviate the condition to such an extent that it’ll not hinder your life in any way. It’ll probably take a few experiments before you find the right remedy. Natural and home treatments for interstitial cystitis can be safely utilized for an effective solution. If you still don’t see any relief, you should consult your doctor right away.
For the natural treatment of interstitial cystitis contact Philadelphia Holistic Clinic (267) 284-4305 to schedule an appointment for the Alternative Holistic Evaluation
Comments
Post a Comment